What is UX design and why is it important
The topic of UX design comes up every time the mobile app development process is discussed. A well-conducted UX research increases your chances of creating a great user’s experience which directly results in increased mobile app profitability.
In this article I will answer the question of what rules you should follow when creating a mobile app so you can design better and more desirable products for users.
Contents
UX design by definition
Simply speaking, User Experience (UX) is the overall experience of a person using a product or service. People usually describe their experience according to value (“Do I get any value?”), function (“Does it work?”), usability (“Is it easy to use?”) and general impression (“Is it pleasant to use?”).
Therefore user experience design is a process to create intuitive, efficient, meaningful and relevant products. This involves a deep understanding of users’ values, needs and abilities. It is an emphatically-driven practice made to solve not only human, but business problems as well. To better understand the idea behind the UX design, let’s take a look at a graph showing the 5 stages of well-known “design thinking”:
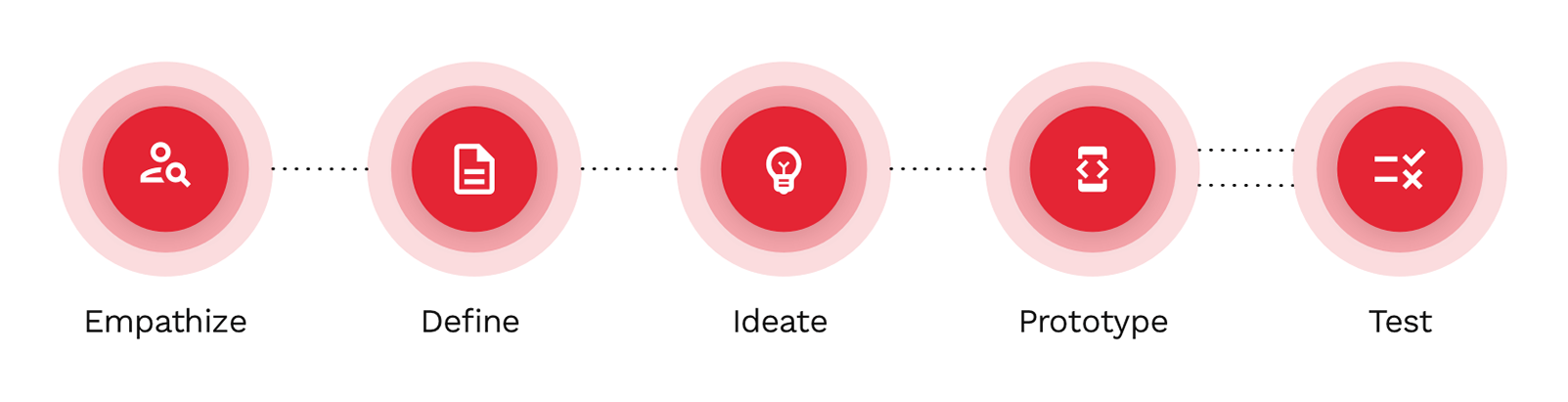
This problem-solving methodology was firstly proposed by the Stanford School of Design and since then it has been considered by designers the cornerstone of good UX design. No matter how varied UX processes can be, it almost always draws from this concept.
Why UX design is important
The reason why UX is so important is that it helps to understand and fulfill the user's needs, and therefore build a better conversion/retention rate. What is more, the valuable UX affects the positive reception of the product and boosts the engagement of users. Defining customer journeys is also helpful in achieving your business goals.
The UX design process
It doesn’t matter what the budget for the project is, or how little time you have, each project of creating a digital product should always follow at least a basic UX strategy. What’s the point of spending time and money on developing a product that does not bring anything new to the market or does not solve any users’ problems? If you want to create good software, you need to combine all the most important components of the UX design process, which includes: product definition, research, analysis, design and validation.
Product definition
This phase is a crucial part of the whole design process. The aim is to understand the product and business as well as you can. It’s all about carefully analyzing all the information obtained from the stakeholders in order to reach the most important conclusions about the product yet to be built. This is a right moment for asking questions like:
- Who are the customers? What are their behaviors? What are their needs and goals?
- What value (quantitative or qualitative) do we commit to offer?
- How will we reach the selected customer segment? Is it online or offline?
- How are we going to attract and retain our clients?
Gather insights, map the value, sketch first mockups. The more you learn, the better the final product will be.
Research
Once you have a clear overview of the project, you can move to market and user research. Only well conducted user testing (with potential users) will answer questions of whether the product development is going in a good direction. Knowing people’s opinion is an invaluable help when working on a digital product.
UX design research methods answer a wide range of questions, but depending on the project, used techniques will vary. You can choose from: focus interviews, IDI (individual in-depth interviews), card sorting, tree testing, field studies and more.
Let’s take a closer look at some of them:
- Focus interviews. This method requires a group of 5-10 people who take part in a moderated conversation conducted by the moderator. This method is especially valuable when you want to learn about attitudes, beliefs or reactions to a particular design or idea.
- On the other hand, in-depth interviews are conversations with only 1 participant. It allows the interviewer to ask more followup questions, catch non-verbal cues and therefore gain a deeper understanding of attitudes and beliefs.
- Card sorting is a highly useful method in creating information architecture. Users are asked to organize certain topics into groups, which is a great way to gasp their mental models and understand how they think about content.
- Tree testing is another useful tool in evaluating information hierarchy in your product. It will help you understand how users navigate your app and what improvements to make to better organize your content.
- There are many ways to conduct field studies. Some of the techniques are based on observation, others may include interviews or interaction with the prototype. However, the most important aspect of field studies is to conduct research activities in the user’s context, not in the office or lab. It is important to observe users in their natural environment.
What is worth remembering is that there is no one-size-fits-all method. You need to understand which problems and questions are there to solve and pick the most suitable research technique that can help you with finding answers.
Analysis
UX design analysis is based on the evaluation of data collected during the research phase. Just as research allows us to find out what users may think and need, analysis allows us to answer the question: why do they need it? Knowing users’ motivation is extremely important to design best solutions and therefore to improve the overall experience.
At this point you most likely need to develop user personas and create storyboards. Creating personas helps to visualize users as specific individuals, not as generic groups of people. Thanks to this, you can define and design the product to aim users’ problems more precisely. You can base it on existing and potential users of your app.
Together with storyboards these are great tools in exploring a user’s experience with a product as well as understanding the flow and feature importance for them. Effective analysis allows you to identify problems and help in the development so that the product serves users even better.
Design
At this point, you should already know the expectations and needs to be met, so you can move into the next phase — design. Creating information architecture and user interface design itself is a process that requires many iterations and validating ideas. It starts with raw sketches to catch main ideas. You can use graphics programs, prepare drawings on paper or blackboard. This is to help with visualizing design solutions, so whatever technique is good for you is just fine. The next step is to prepare wireframes, thanks to which you can see and validate the main structure of the product. This is the core of the project. A high-fidelity project will be created from it, which can then become a prototype to capture the real interaction experience. Well-prepared design guide, which contains all the key information about the visual side of the project, will be of great importance at this stage. It helps not only the UX designers, but also developers to create a coherent visual system.
Testing
The UX design verification is essential to understand if users actually see the value of your product. This is an important step in the process because by acquiring user opinions at an early stage of work, you eliminate some of the risk associated with the future of the product.
There are many ways to evaluate ideas and check their effectiveness. Usually the validation starts in-house. Team members try the product and discover its weaknesses before it is passed to potential users. Once it’s done, the next phase – testing sessions – is to proceed. There is a wide range of techniques of user testing to try, including focus groups, beta testing and A/B testing. There are also surveys to get users’ opinions on specific features and analytics — to uncover the way people interact with the product.
UX vs UI
By this time, you should have a pretty good understanding of what UX design is. But since it is often confused with user interface (UI), let's take a quick look at the roles and differences between UI and UX designers.
Designers who take care of the user interface are responsible for the visual side of the project (visual design). Their task is to develop interface elements, such as buttons, lists, screen transitions and make sure it’s pleasant for the user. Although the interface is a highly important part of the project — UI is about taking care of the visual sensation, the surface of the app, while the UX takes care of the actual usability.
On the other hand, UX designers take care of everything under this surface. They are responsible for the research and for recognizing the needs and expectations of users so that the app’s appearance can primarily serve its function. They answer the question:“How should it work?”, while the UI Designer is devoted to answering “How should it look?”.
Both UI and UX designers should excel with insightful and dynamic thinking to create outstanding products.
Conclusion
It is worth remembering that there is no perfect UX strategy — this is a way of thinking. The methods you use always depend on the project you are working on. Nevertheless, thanks to well-developed UX research, you are able to test whether potential customers actually perceive the value of your product and thus — if your product is desirable. All this contributes to minimizing the risk associated with the release of a new product and brings you closer to achieving your goal: to build a great product for your users.






